MUN Diplomacy and Leadership

In MUN, its not just the quality of the ideas that matter - the quality of the relationships you build that are just as important.
No matter what you do in Model UN, you're going to have disagreements. Fortunately, one of the main goals of MUN is to help you learn how to disagree respectfully. If you don't, it will make your life much more difficult when you want to get your resolutions passed - even if you have the best ideas in the room, people won't vote for you because of how they were treated. Even worse, people might not want to collaborate with you if they don't think they can trust you.
Today, we're going to equip you with the tools to build awesome relationships over the course of your conference, and help you get all of your resolutions passed.
Introducing: The Bloc
'Bloc' is one of those Model UN terms that sounds alot scarier than it actually is - for our purposes, whenever you read 'bloc' just think 'team' and you'll know everything you need.
Teamwork in Model UN
Diplomacy is essential in MUN beyond the resolution-writing process. There are a number of situations where diplomatic skills come into play - these situations are important both if you're working within your bloc or collaborating outside of it.
- Initial Bloc Formation: Building alliances often requires great diplomacy as delegates might share similar goals but differ in their approach or have conflicting minor interests. Diplomacy helps you to bridge these differences and create a collaborative environment.
- Navigating Disagreements: Both within and outside your bloc, there will be moments of friction. For example, this can be your recommended priorities for the committee, or the roles that each delegate will play in the bloc. Diplomacy helps bridge the gap by finding a middle ground or proposing innovative solutions that satisfy everyone.
- Drafting Resolutions: Writing a resolution involves bringing in the opinions of multiple delegates, which can lead to clashes over wording, policy priorities, and strategic direction. Diplomacy is critical in mediating these discussions and ensuring each voice is heard and respected while moving toward a consensus.
Soft-Power Diplomacy

All of the situations we've described will require effective diplomacy to navigate.
But in Model UN you will need to master one specific type of diplomacy - Soft-Power diplomacy. This is a style of diplomacy that relies on persuasion and influence rather than force or coercion.
Unfortunately (or actually quite fortunately), you aren't able to threaten other delegates in your MUN committees with all out war or economic sanctions. Rather, you need to be able to show them how you both succeed if they take your side.
The main benefit of soft power is even if you don't end up agreeing with the other party all the time, there is always some good-will between the groups in any event.
Soft Power is Real Power
Soft Power, in many instances translates to real power on the diplomatic stage. It is now a common indicator of how much influence a country has around the world.
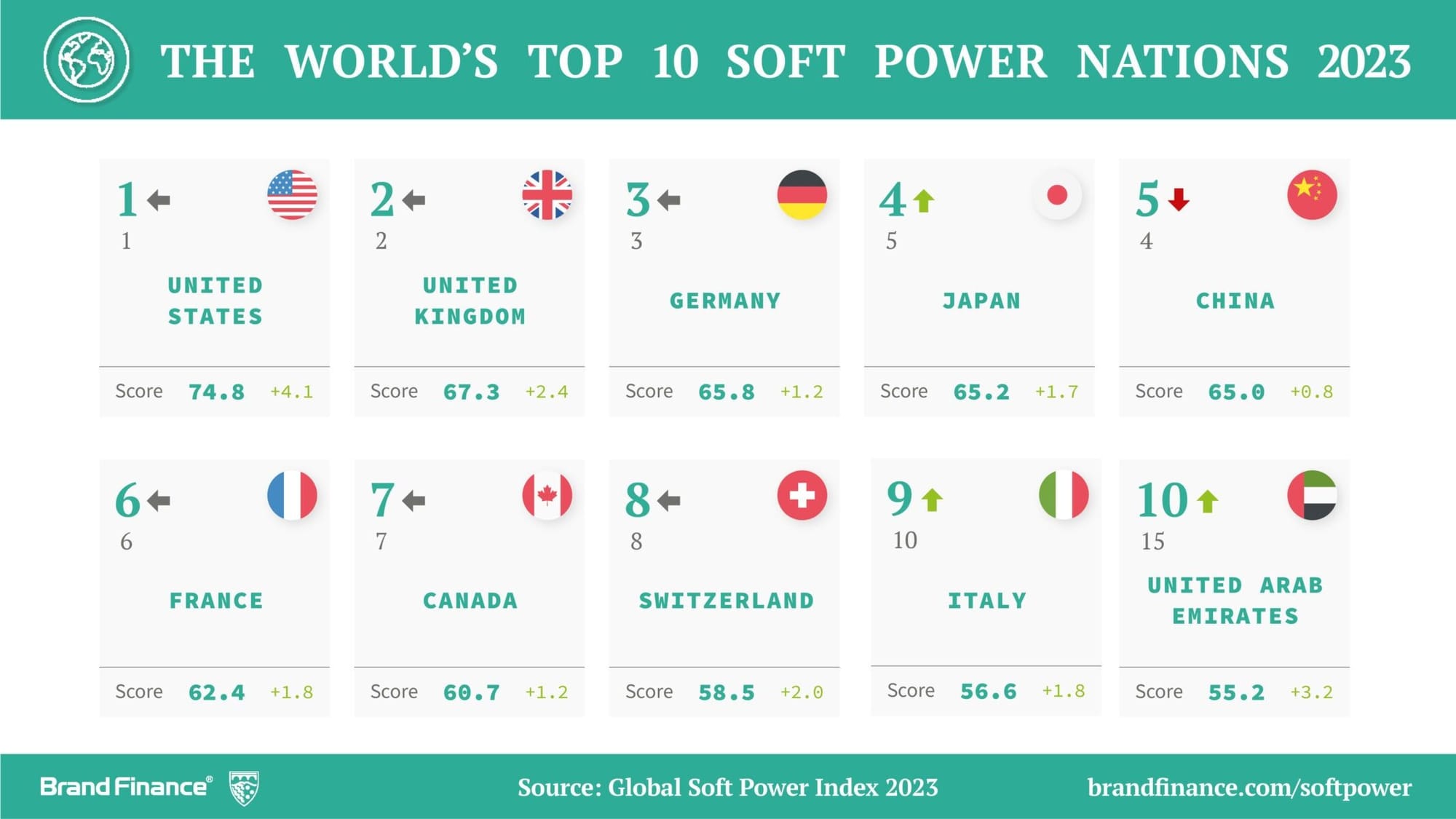
The same applies in Model UN - in your committee, great diplomacy and soft-power skills is not just a courtesy; it is a strategy. Effective diplomats know how to foster trust, mediate tensions, and bring people together.
By using techniques like proposing compromise, active listening, and argument framing, you can lead your blocs to an awesome resolution.
Soft-Power Skills in Model UN
Soft-Power requires a few key attributes, including:
- Empathy and Understanding: Cultivating an understanding of the other party's values, and interests.
- Trust-Building: Building credibility through reliability.
- Transparency: Avoiding hidden agendas to build genuine partnerships.
- Adaptability: Being open to changing tactics when necessary to foster stronger relationships.
Here are a few ways you can leverage your soft-power skills in your next MUN conference.
1. Leverage Shared Goals and Values
Why: Soft power thrives on creating a sense of unity and shared purpose.
How to Use in MUN:
- Highlight common goals that resonate across blocs: “Many of us are committed to addressing climate change. Let’s draft solutions that reflect that shared responsibility.”
- Appeal to universal values, such as human rights or sustainable development, to draw diverse nations into your coalition.
2. Build Alliances Through Recognition
Why: People are more likely to support those who recognize their strengths.
How to Use in MUN:
- Compliment another delegate’s idea publicly: “The delegate of [country] has made an excellent point regarding resource allocation.”
- Saying something encouraging about a delegates work or speech shows that you appreciate their contributions.
3. Use Soft Power Symbols
Why: Using real-world examples can sometimes help add to your position on a matter.
How to Use in MUN:
- Reference international agreements your country has supported, showing your commitment to global cooperation: “As a signatory of the Paris Agreement, my country believes…”
- Offer compromises or resources (symbolically) as a way to lead by example: “We are willing to commit to an additional clause on financial aid if it strengthens our shared proposal.”
4. Position Yourself as a Consensus Builder
Why: Delegates who bridge divides wield significant influence.
How to Use in MUN:
- Present yourself as a mediator: “I see that both sides have valid points—let’s combine these ideas to create a stronger resolution.”
- Offer solutions that appeal to both opposing and neutral blocs, framing them as mutually beneficial.
Sounding Like a Diplomat
Along with these key skills. Diplomatic language can go a long way in expressing your ideas properly. It is designed to avoid conflict, foster cooperation, and maintain positive relationships.
Here are some examples of diplomatic language that you can use:
- Making Suggestions
- Instead of: "Your plan is flawed and won’t work."
- Diplomatic: "Perhaps we could explore alternative approaches to address the issue more effectively."
- Expressing Disagreement
- Instead of: "You’re wrong."
- Diplomatic: "I see things differently and believe there might be other factors to consider."
- Requesting Clarification
- Instead of: "What you said doesn’t make sense."
- Diplomatic: "Could you please elaborate on that point to help us understand better?"
- Offering Compromises
- Instead of: "We won’t agree to this."
- Diplomatic: "We are willing to consider your proposal with some modifications. Perhaps we can find a middle ground."
- Expressing Concerns
- Instead of: "This will never work."
- Diplomatic: "We have reservations about the feasibility of this approach, but are open to further discussion to find a solution."
- Proposing Future Actions
- Instead of: "We can’t move forward with this."
- Diplomatic: "To move forward constructively, it might be helpful to establish a working group to explore these issues in more depth."
Learn More - Famous UN Diplomats
Kofi Annan (Ghana)
- Background: Annan served as the 7th Secretary-General of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. His tenure included initiatives focusing on comprehensive reform of the UN and work on issues like HIV/AIDS, combating terrorism, and promoting human rights.
- Legacy: He was a co-recipient of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize for revitalizing the UN and emphasizing its global responsibility.
Gro Harlem Brundtland (Norway)
- Background: Brundtland was the former Prime Minister of Norway and later became the Director-General of the World Health Organization (WHO). Although not a UN Secretary-General, her role in global governance and her advocacy for sustainable development have had a lasting impact.
- Legacy: She chaired the World Commission on Environment and Development, which produced the landmark Brundtland Report, defining sustainable development as "development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs."
Boutros Boutros-Ghali (Egypt)
- Background: Boutros-Ghali was the 6th Secretary-General of the United Nations, serving from 1992 to 1996. He presided during a tumultuous time that included crises in Somalia, Rwanda, and the former Yugoslavia.
- Legacy: He is known for authoring the “An Agenda for Peace” report, which laid out a framework for preventive diplomacy, peace-making, and peacekeeping.
Dag Hammarskjöld (Sweden)
- Background: Hammarskjöld was the second Secretary-General of the United Nations, serving from 1953 until his death in 1961. He is often remembered for strengthening the UN’s role in international diplomacy and peacekeeping, particularly during crises such as the Congo crisis.
- Legacy: Known for his dedication to peace and neutrality, Hammarskjöld was posthumously awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1961.






